Abstract
Acquired or de novo resistance to the traditional and novel anti-multiple myeloma (MM) agents remains a major treatment obstacle, therefore novel therapies are in need. Wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 (WIP1) is an oncogenic serine/threonine phosphatase implicated in silencing of cellular responses to genotoxic stress. WIP1 overexpression was documented in various solid cancers in correlation with aggressive features and poor prognosis. Thus, we studied WIP1 in MM addressing its potential role in mediating resistance and aggressive phenotype.
Increased expression of WIP1 was detected in MM cell lines (n=8) and primary samples (n=18) at both mRNA and protein level as compared with normal PBMCs (n=5). Furthermore, a positive correlation between WIP1 and CXCR4 levels (p<0.02, R2=0.5) was revealed. The latter is a well-known oncogenic receptor in MM. WIP1 expression levels were significantly up-regulated following bortezomib (Bort) treatment. Using MM cell lines with acquired resistance to Bort (RPMI8226BortRes and CAGBortRes), a higher induction of WIP1 upon Bort exposure could be demonstrated, suggesting a possible role for WIP1 in the acquisition of MM drug resistance to proteasome inhibitors. WIP1 was also upregulated in MM cells cultured on human BM stroma (BMSC) known to protect the tumor cells from Bort-induced apoptosis, further supporting its function in mediating resistance.
GSK2830371 (GSK), a novel allosteric inhibitor of WIP1, significantly suppressed MM cells proliferation (p<0.01) and induced apoptosis, as demonstrated by phosphatidylserine externalization, mitochondrial depolarization (ψm), caspase 3 and PARP cleavage, and DNA fragmentation. Moreover, combined treatment with GSK and Bort synergistically potentiated cell death in both Bort-sensitive and resistant MM cells and overcame BMSC protection (CI<0.5). The robust apoptosis induced by Bort/GSK treatment was accompanied by increased mitochondrial ROS accumulation, subsequent mitochondrial destabilization and extensive DNA damage. GSK treatment resulted in a reduction of WIP1 basal expression and abrogated WIP1 induction upon Bort treatment. Thus, we defined that GSK can regulate WIP1 expression in MM cells.
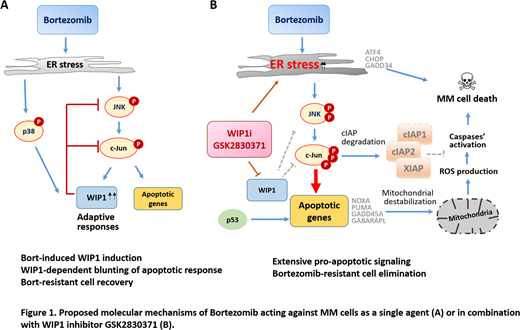
To determine the molecular mechanism of Bort/GSK synergism we performed gene and protein expression analysis. Combination of both agents significantly reduced expression of anti-apoptotic proteins such as cIAP1, cIAP2, XIAP and Survivin. Previous studies indicate that maintaining IAPs expression is part of an adaptive unfolded protein response that promotes MM survival upon Bort-induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Therefore, it is conceivable that targeting IAPs upon WIP1 inhibition may overcome protective responses, inducing unresolved ER stress and MM cell death.
Indeed, we found that combination of Bort and GSK significantly enhanced ER stress, as indicated by increase in the pro-apoptotic factors ATF4, CHOP and GADD34. Concomitantly, mitosis-inducing factors Cyclin B1, CDK1 and PLK1 were prominently reduced upon Bort/GSK treatment.
To assess the potential role of p53 activation in GSK-mediated effects, p53-stabilizing agents nutlin3a and PRIMA1 were applied in combination with WIP1 inhibition. We observed a significant (p<0.01) increase in the responsiveness of both p53WT and p53mut MM cells to GSK-mediated apoptosis. Consistently, combined GSK/Bort treatment upregulated p53 targets, including PUMA, NOXA, GADD45A and p21 genes. These data suggest that p53 may potentiate the WIP1 inhibition mediated stress induction.
Finally, we assessed the signaling pathways that may be involved in WIP1 mediated cessation of stress response. GSK profoundly augmented Bort-induced phosphorylation of JNK and c-Jun, without affecting p38 phosphorylation. Accordingly, JNK inhibitor SP600125 successfully reverted both the apoptosis and the downregulation of IAPs induced by Bort/GSK treatment. Altogether, these results identify pro-apoptotic JNK/c-Jun signaling being preferential target of WIP1 in the process of dampening Bort-induced stress response.
To conclude, we disclose the role of WIP1 in blunting stress response and promoting resistance to bortezomib. Collectively, WIP1 suppression prevents MM cell adaptation and recovery upon ER stress. These findings may provide the scientific basis for a novel combinatorial anti-myeloma therapy.
Peled:Cellect Biotherapeutics Ltd: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal